Utilization Of Nano emulsions In Tomato Preservation
- Arunpravin R S

- Mar 5, 2025
- 3 min read
Introduction
Tomatoes have a limited shelf life at room temperature, are a highly perishable fruit, and change continuously after harvesting. Tomatoes, as a climacteric and perishable produce, have a relatively short life cycle, usually 2 to 3 weeks. Researchers began investigating their potential as bioactive component delivery methods, such as vitamins and antioxidants, to increase the shelf life and stability of food goods.
Researchers began investigating their potential as bioactive component delivery methods, such as vitamins and antioxidants, to increase the shelf life and stability of food goods. In some places, using Nanoemulsions in food products has caused regulatory concerns as authorities work to ensure their safety for ingestion. Nanoemulsions are still a hot topic in the food business, with continuous attempts to investigate their potential for increasing the shelf life of a wide range of products while meeting regulatory standards and consumer preferences.
Discovering The Wonders of Oil Emulsion
The integration of essential oils (EOs) as natural antibacterial agents in edible coatings has recently gained increased attention to minimize deterioration and improve the storage life of perishable foods. When applied to tomato fruit, an antimicrobial coating formulation based on sodium alginate cross-linked with calcium chloride at different concentrations and dipping time was optimized as a function of coating thickness. To suppress the growth of the endogenous.
The Great Impact of Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Cardamom
It helps maintain the stability of the emulsion, preventing phase separation and ensuring a consistent distribution of cardamom oil droplets. This nano-sized emulsion has several advantages for tomato preservation: The nano-emulsion enhances the solubility and dispersion of cardamom oil in the tomato product, ensuring uniform distribution. Cardamom oil's antimicrobial properties help extend the shelf life of tomato products by inhibiting microbial growth and delaying spoilage.
typing
Exploring The Effects of Nano-Emulsion of Piper Betel Leaf
Piper betel leaf essential oil nano-emulsion with hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) as an antibacterial and bioactive chemical. It also sought to maximize the extraction of essential oils (EO) from Piper betel leaves, which include medicinal, antibacterial, and antioxidant chemicals such as chavicol, eugenol, and others. The essential oils were extracted, and a nano-emulsion was created using a low-energy emulsification method and mixed into an edible HPMC composite to see if the edible coatings of the Piper betel leaf nano-emulsion might postpone the changes that cause fruit deterioration. When compared to uncoated control fruits, the coverings delayed 5% changes in color, 8% weight loss, titratable acidity, ascorbic acid content, soluble solids concentration, lycopene, and decay percentage.
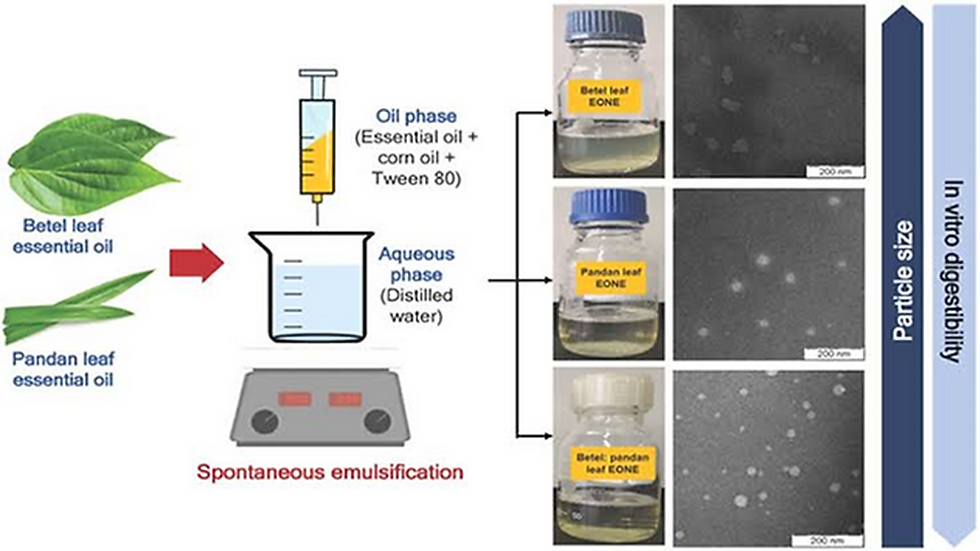
Edible nano-emulsion coatings containing sweet orange essential oil and sodium alginate were prepared and characterized, then tested for antibacterial and antibiofilm activity against Salmonella and Listeria, as well as the coating effect on various quality characteristics of tomatoes at 22 2 °C for 15 days. DLS (Dynamic light scattering) analysis demonstrated a stable Nanoemulsions formulation with a 43.23 nm particle size. The high whiteness index of Nanoemulsions improves product marketability and desirability. Antibacterial and antibiofilm investigations demonstrated that Nanoemulsions efficiently eradicated both sessile and planktonic forms of Salmonella and Listeria in single and multi-species culture settings

A Closer Look at The Trends in Usage
Consumers' growing desire for a healthy diet has spurred researchers to develop cutting-edge technologies for preserving the freshness of fruits and vegetables without the use of preservatives. Nanoemulsions have been recognized as an efficient and most appropriate form of technology in the agro-food industry. Edible Nanoemulsions could address market demand for vegetables, fruits, drinks, food packaging, and dairy products.
Fun Facts!
1. Nanoparticles have been attached to textile fibers to create smart and functional clothing
2. Nanoparticles were used by artisans as far back as Rome in the fourth century in the famous Lycurgus cup made of dichroic glass as well as in the ninth century.
3. Nanoparticles are naturally produced by many cosmological, geological, meteorological, and biological processes.
Conclusion
Oregano essential oil has several benefits for preserving tomatoes, such as its natural origin, antibacterial and antioxidant properties, and flavor enhancement. Piper betel essential oil in tomato preservation can offer natural antimicrobial and flavor-enhancing benefits, but it also comes with challenges such as flavor overpowering, formulation complexity, regulatory considerations, and cost implications. Citrus sinensis essential oil Nanoemulsions offer numerous advantages, including flavor enhancement and antimicrobial properties. However, they also come with certain disadvantages, such as formulation complexity, shelf-life stability concerns, and regulatory considerations.
Author:
Joshita. B
Blogger
Undergraduate Student at SRM
References
Image Credits



Comments